1. Collection, processing and storage of serum in ELISA experiments;
1. Vacuum blood collection needle collects 2ml fresh blood and is added to the sterile test tube;
2. After standing at room temperature for 1 hour;
3, the blood was collected using a centrifuge 4 ℃, 25 00r pm centrifuged 10min ,, good homogenate is centrifuged supernatant left, below precipitate discarded.
4. Take the supernatant. Pack and store frozen,
Store at 24-8 ° C for 24-48 hours ;
- Store at 20 °C for 1 month;
Store at -70 °C for 6 months;
5, according to your experimental needs, take appropriate amount of supernatant to carry out various ELISA measurements.
Most ELISA tests use serum as a specimen. Serum samples can be collected according to conventional methods. Care should be taken to avoid hemolysis. When red blood cells are dissolved, substances with peroxidase activity are released. In ELISA assays marked with HRP, hemolyzed specimens may increase non-specific coloration. In addition, bacterial contamination should be avoided, as the cells may contain endogenous HRP and may also produce false positive reactions. Serum samples should be tested fresh. If stored in the refrigerator for a long time, the polymerization can occur, and the background can be deepened in the indirect ELISA.
Second, the collection, processing and preservation of plasma in ELISA experiments;
1. Vacuum blood collection needle collects 2ml fresh blood and is added to the sterile test tube;
2. Add anticoagulant (EDTA, sodium oxalate, heparin, sodium citrate) at 1:9 , and separate the plasma on ice to reduce platelet contamination within 30 minutes; (can also be collected directly with anticoagulation tube ) ;
3, the blood was collected using a centrifuge 4 ℃, 25 00r pm centrifuged 5min ,, good homogenate is centrifuged supernatant left, below precipitate discarded.
4. Take the supernatant. Pack and store frozen,
Store at 24-8 ° C for 24-48 hours ;
- Store at 20 °C for 1 month;
Store at -70 °C for 6 months;
5, according to your experimental needs, take appropriate amount of supernatant to carry out various ELISA measurements.
Please note that there are special requirements for anticoagulants in the indicator sheet. EDTA is recommended . In addition to fibrinogen and anticoagulant, the plasma is equivalent to serum.Note: Preparation of plasma specimens requires the use of the anticoagulant EDTA, and specimens with incomplete anticoagulation cause false positives due to fibrinogen interference .
3. Collection, treatment and preservation of urine in ELISA experiments ;
1. Collect 500ul of urine sample and add it to the sterile test tube;
2, the blood was collected using a centrifuge 4 ℃, 25 00r pm centrifuged 10min ,, the supernatant was centrifuged good sample left, below precipitate discarded.
3. Take the supernatant. Pack and store frozen,
Store at 24-8 ° C for 24-48 hours ;
- Store at 20 °C for 1 month;
Store at -70 °C for 6 months;
4, according to your experimental needs, take appropriate amount of supernatant to carry out various ELISA measurements.
4. Collection, processing and preservation of cerebrospinal fluid in ELISA experiments ;
1. Collect cerebrospinal fluid samples and add them to sterile test tubes;
2, the blood was collected using a centrifuge 4 ℃, 25 00r pm centrifuged 10min ,, the supernatant was centrifuged good sample left, below precipitate discarded.
3. Take the supernatant. Pack and store frozen,
Store at 24-8 ° C for 24-48 hours ;
- Store at 20 °C for 1 month;
Store at -70 °C for 6 months;
4, according to your experimental needs, take appropriate amount of supernatant to carry out various ELISA measurements.
5. Collection, processing and preservation of cell supernatant in ELISA experiments;
1. Collect 500 ul of cell culture supernatant and add to sterile test tubes;
2, the blood was collected using a centrifuge 4 ℃, 25 00r pm centrifuged 10min ,, left homogenate supernatant is centrifuged good
Colorful Mottled Waxy Corn is generally white, yellow, red, purple and black, with white, yellow and Black Waxy Corn being the basic colours. The purple gene of a purple-white cross naturally becomes purple if it "beats" the white gene, and vice versa, so if the two make a tie, we see white and purple corn. Purple can turn into red and Fresh Black Corn, or as we often say, "red is purple and black is purple". Of these Mottled Waxy Corn, the most common Yellow Waxy Corn is the most nutritious, as it is rich in carotenoids.
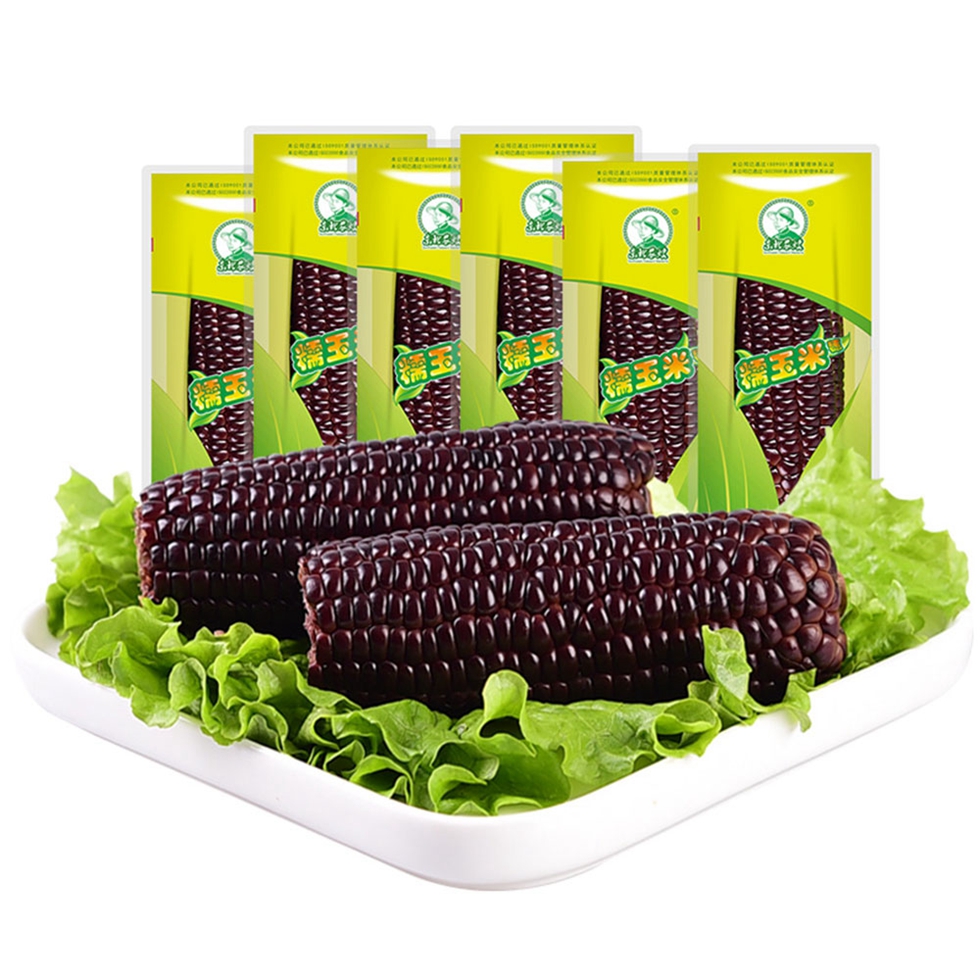
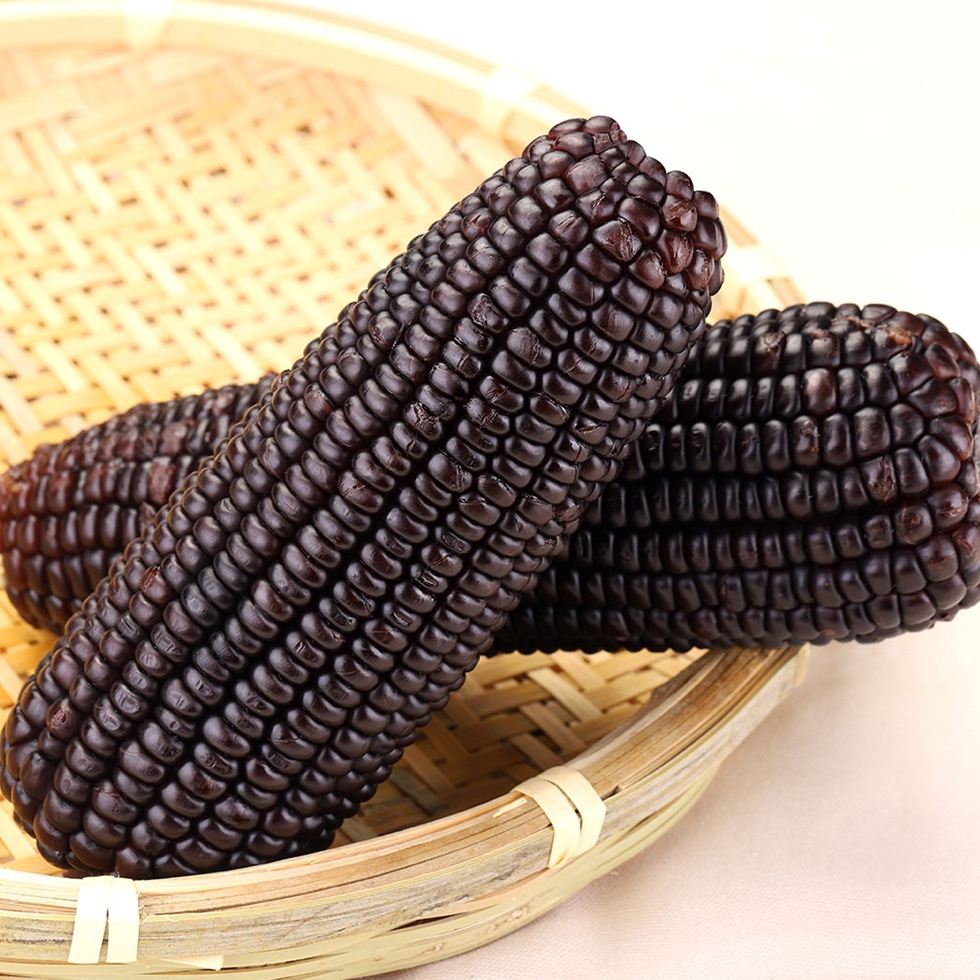


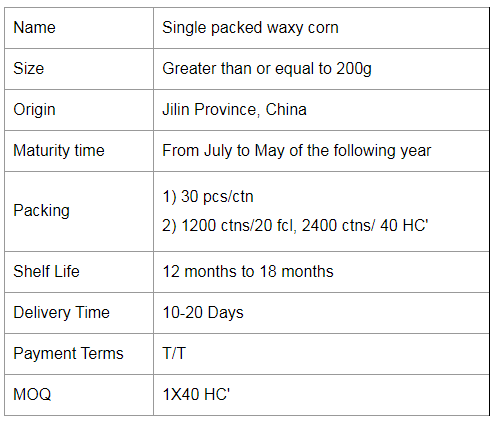
Purple Waxy Corn,Single Packed Waxy Corn,Single Packed Black Waxy Corn,Single Packed Purple Waxy Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com