A new method for the high specificity of plants against DNA viruses established by genetic development
December 18, 2018 Source: Chinese Academy of Sciences
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];Geminiviruses are the only single-stranded DNA viruses found in plants that have the morphology of twin particles and are the largest family of single-stranded DNA viruses known to date. According to ICTV (International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses), the virus has been increased to nine genera, and it has a wide host in monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants, which is harmful to agricultural production. The traditional research on disease resistance mechanism is mainly based on the analysis of viral gene function and the analysis of host virus interaction mechanism, but the application in breeding is still limited. The Gao Caixia research group of the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences previously used the adaptive immune system CRISPR/Cas9 derived from bacteria to specifically recognize the characteristics of the cutting virus and foreign DNA, and the beet severe curly top BSCTV (Beet severe curly top) Virus is a model virus, and the model plants Nicotiana benthamiana and Arabidopsis thaliana are selected as host materials, and a new, simple and efficient geminivirus defense system has been established in plants (Ji et al, Nat). Plants, 2015).
However, off-target (ie editing of non-target sites) is a major drawback of the CRISPR/Cas9 system for gene therapy and molecular breeding. There are two main factors that lead to off-target. The first is the fault tolerance of sgRNA sequences. It has been reported that the tolerance of sgRNA in animal cells can be as high as 5 bases; the second is that continuous expression of Cas9 protein is likely to cause cleavage of non-target sites. Thus, the antiviral system based on the overexpression of the CRISPR/Cas9 system is likely to undergo off-target modification of the plant genome. In this study, Gao Caixia's team targeted the disease-resistant Arabidopsis overexpressing the CRISPR/Cas9 system and found 10 potential off-target sites on the Arabidopsis genome at the high antiviral target site (C3) ( 3 or 4 base mismatches). The results of the second-generation sequencing analysis showed that 8 of the 10 potential off-target sites had off-target modification. Thus, although the overexpressed CRISPR/Cas9 system is highly resistant to geminiviruses, it is also susceptible to off-target modification in the genome of plants. Therefore, the researchers used a virus-inducible promoter of the geminivirus (BSCTV) to construct a new virus-inducible genome-editing system (VIGE) to avoid the continuous expression of Cas9. Reduce the occurrence of off-target events. The results based on the GUS reporting system indicate that the system can respond synchronously to the activation induction of BSCTV. Moreover, the transient screening system based on N. benthamiana and transgenic Arabidopsis plants indicate that the virus-inducible genome editing system can be effectively activated and inhibit the accumulation of BSCTV in host plants. By off-target analysis of different tissues of transgenic Arabidopsis plants before and after BSCTV infection, the second-generation sequencing results showed that the system has high specificity in transgenic plants. In view of the widespread presence of such virus-inducible promoters in the genome of the geminivirus, this method can be applied to the cultivation of antiviral plants.
The study was published online November 15 in the journal Genome Biology (DOI: 10.1186/s13059-018-1580-4). Gao Xiangxia's Ph.D. student Ji Xiang and Si Xiaomin are the co-first authors of the article. The study was funded by the GM Special Project, the Foundation Science Center of the Fund Committee, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
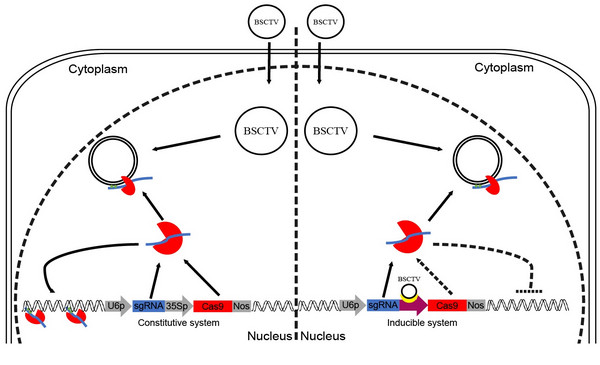
Virus Induced Genomic Editing System (VIGE) pattern diagram
Chloride is a common inorganic anion in water and wastewater. Chloride ions are found in almost all natural water,and their levels vary widely. In rivers, lakes. In marshes, chloride levels are generally low,but in seawater,salt lakes,and some groundwater levels can be as high as tens of grams per liter. In the human survival activities,chloride has very important physiological functions and industrial uses.Because of this,a considerable amount of chloride ions are contained in domestic sewage and industrial wastewater.
If the content of chloride ion in the book reaches 250mg without litres,the corresponding cation is sodium,will feel salty; High levels of chloride in water can damage metal pipes and buildings and hinder plant growth.
Water Chloride Test Strips,Chloride Test Strips,Water Chloride Test Kits,Wastewater Water Test Kits
Changchun LYZ Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.lyzinstruments.com