Release date: 2018-01-24
The DNA nano-robot system is one of the nanomachines and has been continuously developed in recent years. In the January 19 issue of Science, we saw another "feat" in DNA nano-robots - researchers used electric fields to accelerate the speed of DNA robot systems.
The previous DNA molecular machine could not run faster because it relied on DNA molecular factors. By contrast, this DNA molecular robot is about 100,000 times faster than ordinary DNA robots. It can be said that it is extremely large. Promoted the development of DNA robot systems.

The study was done by a team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) in Germany. The collaborator of the paper, Professor Friedrich Simmel of the Technical University of Munich (TUM), said that most of the previous DNA-based machines were mainly regulated by a variety of DNA molecules, including the use of additional external DNA "fuel chain" DNA hybridization. , DNA-cleaving enzymes, changing the buffering environment (such as pH), or using chemical photoelectric switches to collect light to induce the reaction. However, for a variety of reasons, these methods ultimately make the exercise very slow and take minutes or even hours to complete the desired exercise process.
Compared to the previously demonstrated DNA robotic system or assembly line, this result uses electric field control to move and position the DNA machine faster, and the method does not require the addition of any "fuel" or changes to the buffering environment.
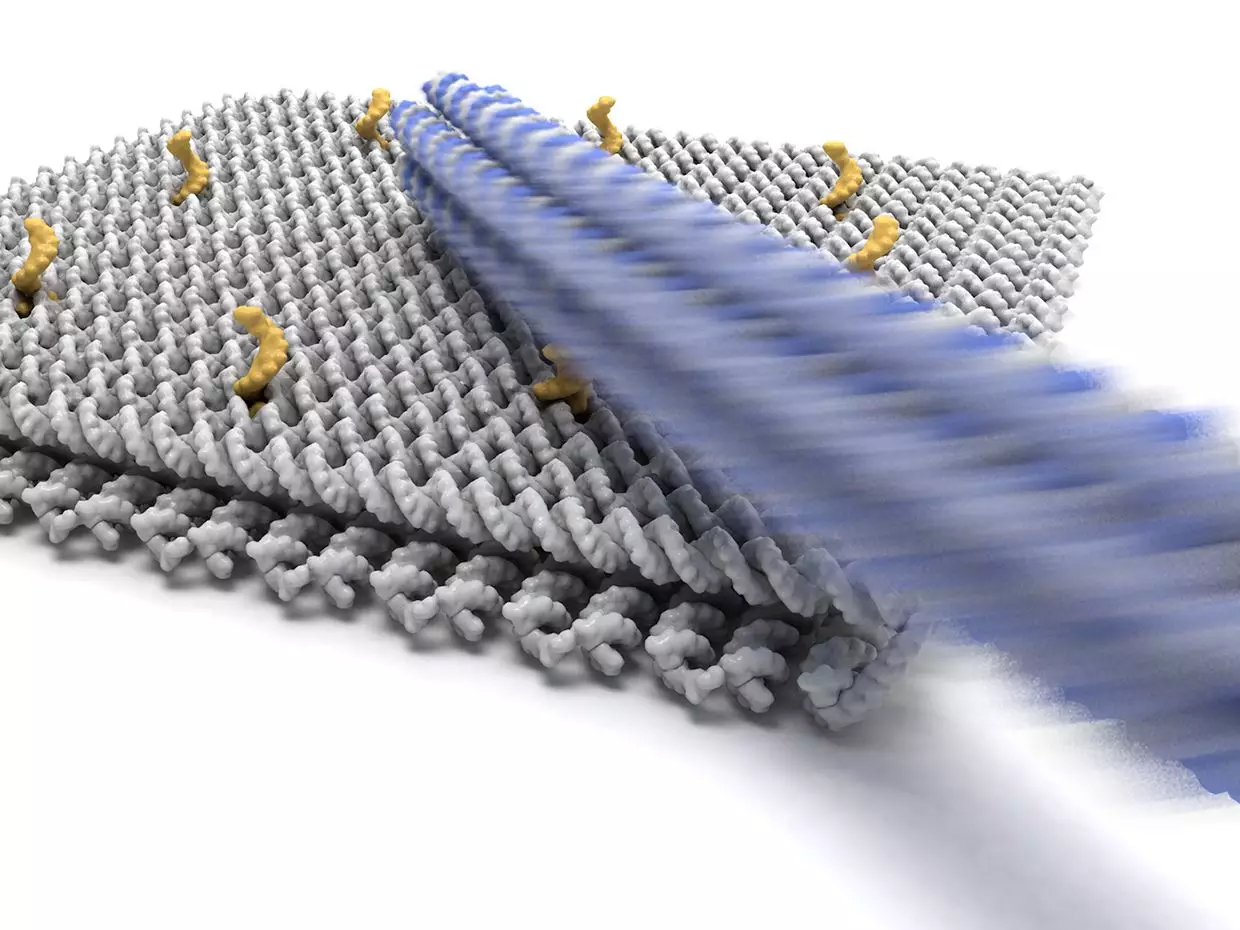
In this experiment, Simmel and his colleagues used a technique of molecular self-assembly: DNA origami. This technique folds the DNA strand into a clever structure.
Using DNA origami technology, the team created a square rigid base with a side length of 55 nanometers connected by a flexible joint to a long arm of 25-400 nm (the structures involved are composed of DNA molecules). The structure is fixed to the bottom of a custom-filled sample chamber where researchers can apply an electric field in any direction to the rigid base.
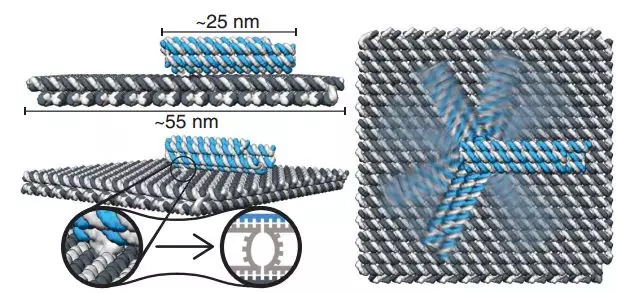
The left picture shows the square base and the mechanical arm that are “folded†by the DNA “folding†technique, and the joints connecting the two; the right picture shows the application of force to the end of the mechanical arm under the action of the electric field. Rotate around the node axis
Because DNA is negatively charged, it can be manipulated by the electric field. By controlling the direction of the DNA, the researchers can make the DNA arm make any angular motion relative to the substrate. In addition to the rapid regulation of DNA, the electric field can also be used to reduce the stability of DNA docking, thereby speeding up the unbinding of DNA arms immobilized on the substrate.

Clockwise and counterclockwise movement of the robot arm at 25 Hz
Simmel adds that when creating “docking points†on the substrate, the electric field can be used to move the DNA arm from the fixed position on the substrate to another position. In addition, when the DNA arm is fixed to a specific pair of ground, if the binding point is fixed enough, even if we remove the electric field, the DNA arm can be well fixed at that point.
An important feature of the system is that the DNA arm can act as a "pointer" for a fixed point of view or as a lever arm. When a large amount of charge is carried on the DNA arm, the external electric field exerts a large force on it, and this force can cause the DNA arm to rotate around the fulcrum or achieve docking with the node.
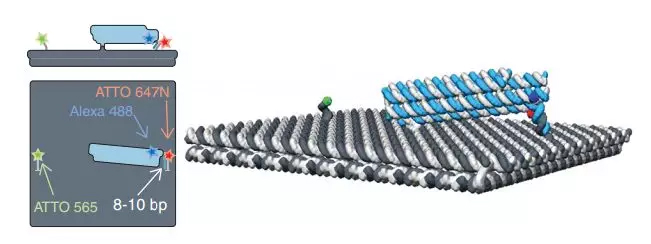
After assembling the robotic arm, the researchers placed a 25 nm gold particle on the freely movable end of the DNA arm. After the external electric field is turned on, the DNA robot arm begins to rotate, causing the top nanoparticle to move.
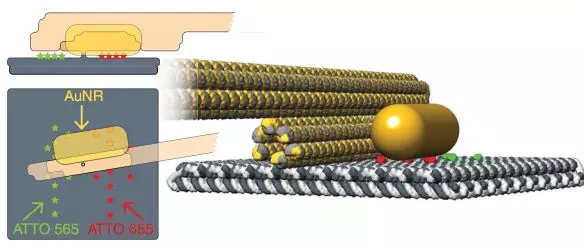
The 丨 researchers put a gold nanorod on the arm, which drives it to interact with the fluorescent substances (green and red) on the base.
Although it has been very meaningful to determine the operating mechanism of the DNA arm, Simmel's research team has a larger goal. Next, they will continue to work on how to use the DNA arm to create a reliable mechanism for grabbing and releasing molecules/nanoparticles, moving objects from the acquisition area to the target (target) area through the arm.
The DNA arm can also be used in conjunction with other technology platforms to pick up and release RNA or DNA polymerases of the constructed molecule to achieve 3D printing of biomolecules at the atomic level. Simmel also believes that the way in which complex molecular structures are assembled in a potential application of the study may be somewhat similar to a 3D printer. Although it is impossible to quickly print 3D molecules, this work opens up new directions for the regulation of DNA nanodevices. In addition, the remotely controllable DNA arm is also suitable for the preparation of drug molecules for precise drug release at the molecular level.
Source: DeepTech Deep Technology (micro signal mit-tr)
Cleaned Squid Tubes,Frozen Squid Tube,Frozen Cleaned Squid Tubes,Stuffed squid tubes
ZHOUSHAN JING YUAN FOOD CO.,LTD , https://www.genho-food.com