According to the World Bank, the world medical market in 2005 was about $4.6 trillion, an average of 7% per year, and reached about $7.3 trillion by 2012. As the medical market has expanded dramatically, the world's medical giants have begun to provide super-crossing medical services. Among them, the Chinese market with more than 1.3 billion people has become the main target.
According to the report, IHH Healthcare Bhd, the largest hospital operator in Asia, said that “10 years later, half of the hospital sales will come from Chinaâ€. Medical giants are targeting China's rapidly growing medical costs. At present, China's per capita medical expenses are only ranked 93rd in the world, but will grow rapidly with the increase of income in the future. Some analysts pointed out that in 2007 China's per capita medical expenses were 113 US dollars, and by 2012 it was 321 US dollars, with an average annual growth rate of 23.2%.
According to the report, China's rapidly growing medical needs are related to demographic changes. In 2012, China's elderly population over the age of 65 accounted for 8.67%, which has met the 7% standard requirements of an aging society. On top of this, with the increase in income, the spread of infectious diseases caused by the migration of the working population, and the concern about health caused by profound environmental problems, China's demand for advanced medical services is also increasing. The number of adult patients is also growing rapidly. The number of people with diabetes last year was about 98.4 million, and it is expected to reach 140 million by 2035. If medical demand expands rapidly at this rate, China will only actively import hospitals from overseas.
For example, the Chinese government began to notice that the increasing demand for medical demand began in 1989. In that year, the government allowed overseas Chinese hospitals to set up hospitals in China and opened up the domestic medical market. In 2000, there were many restrictions on the establishment of medical corporations by foreign capital, but the remaining restrictions were all lifted in 2012. Taking this opportunity, Sichuan Province allows foreign investors to invest up to 90%, including seven places including Shanghai, Beijing, and Hainan, which will allow foreign investors to set up private hospitals this year.
In response, foreign medical giants started the operation early, including IHH Healthcare Bhd. The company focuses on the Mount Elizabeth hospital in Singapore and expands its operations in major Asian regions. According to statistics, IHH Healthcare's company market value ranks second in the world, second only to the US HCA company.
According to reports, hospitals in countries and regions such as the United States are also participating in the Chinese market. Chindex International, Inc., a Nasdaq-listed company in the United States, has entered the Chinese market through corporate mergers since 1997. After the loosening of medical regulations, the first foreign-funded hospital in China, Hejia Hospital, was established in cooperation with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. The current business has expanded to 17 clinics and 1 large hospital in China. The hospital's sophisticated inspections have attracted China's affluent class, with an average medical treatment time of 20 or more. The initial diagnosis is more than 1 hour, but the fee is not cheap, only the initial consultation costs $200.
In Taiwan, 22 hospitals in Taiwan have entered the Chinese mainland market. Among them, Chang Gung Hospital in Taiwan operates 2,000 beds in Xiamen, Fujian, and operates 1,000 beds in Beijing. Due to the same language and culture, Chang Gung Hospital hopes to expand its market share in mainland China as soon as possible.
The report also pointed out that Japan has also recently joined the "war." In August last year, Japan established the Health Care Strategy Promotion Headquarters, which was headed by Prime Minister Shinzo Abe. The company has eight promotion agencies, one of which is the Medical Internationalization Promotion Group. The goal is to explore new markets such as China, Russia and Myanmar.
New product of U85 micro laser distance sensors use highly focused class 2 laser to detect objects or measure distances, and can return a measured value via varieties intface( serial, usb, rs232, rs485, bluetooth etc.). The electronic distance sensor is a very small Laser Distance Sensor, but high resolution up to 1mm and long distance measuring sensor - teachable measuring range of up to 30m. Extremely accurate distance sensing sensors, errors down to ± 1mm. And the mini sensors and measurements support continuous measurement function, great for compact solutions(eg: robots) with the smallest Laser Distance Sensor of the world!
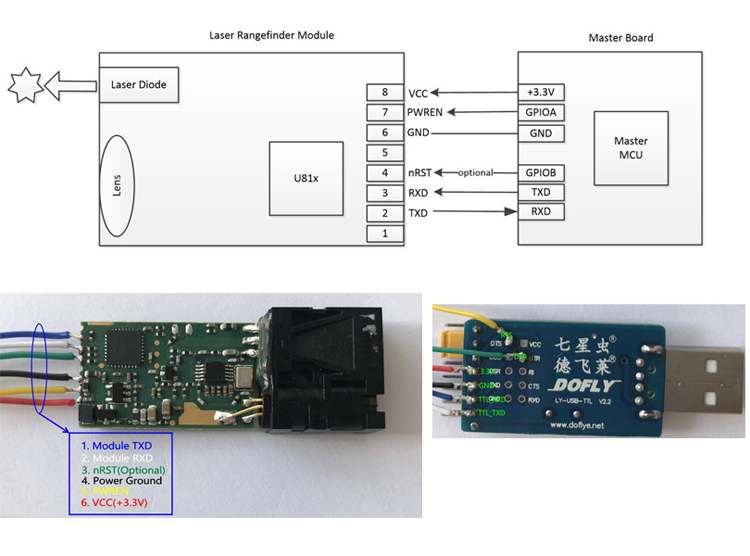
Parameters of U85:
Accuracy
±1 mm (0.04 inch)
Measuring Unit
mm
Measuring Range (without Reflection)
0.03-20m/0.03-30m
Measuring Time
0.1~3 seconds
Laser Class
Class II
Laser Type
620nm-690nm, <1mW
Size
41*17*7mm (±1 mm)
Weight
About 4g
Voltage
DC2.0~3.3V
Electrical Level
TTL/CMOS
Certifications
CE, FCC, RoHS, FDA
Operating Temperature
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
Storage Temperature
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
Mini Laser Distance Sensor,Optical Laser Distance Sensor,Smallest Laser Range Sonsor,Laser Measuring Sensor
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jrt-measure.com